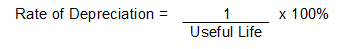Straight line depreciation

| Cost | Initial acquisition or construction costs related to the asset, as well as any subsequent capital expenditure. |
| Residual Value | Residual value is the estimated proceeds from the disposal of an asset at the end of its useful life. Residual value is also known as its scrap, or salvage value, The portion of an asset's cost equal to the residual value is not depreciated because it is expected to be recovered at the end of an asset's useful life. |
| Useful Life | The estimated time period that the asset is expected to be used, starting from the date it is available for use up until the date of its disposal or termination of use. Useful life is normally expressed in years or months. |
| Rate of Depreciation |
The percentage of useful life that is consumed in a single accounting period. The rate of depreciation is calculated as
The depreciation expense needs to be adjusted downwards when an asset is acquired or disposed of during the accounting period to avoid distributing depreciation for the time when the asset was not available for use. |
Advantages
- Easy to calculate.
- Useful when the pattern of economic benefits are hard to determine with precision.
- Suitable for depreciating assets that provide similar levels of economic benefits throughout their useful life (for example, buildings).
Disadvantages
- May not reflect the true pattern of an asset's economic benefits.