
A diesel truck converts the energy in diesel fuel into wheel motion. There are several stages involved in this process, as shown below.
Each stage introduces inefficiencies in the conversion of energy. The efficiency of diesel-powered systems varies, in the range of 30% to 40%. The conversion of hydrogen fuel cells also varies; it is typically higher at 40% to 60%. The tables below contain information about the specific energy of the two fuel sources used in our calculations. RPMGlobal recommends sourcing information on fuel usage directly from the manufacturer. If fuel usage information is unavailable from the manufacturer, you could use the calculations below instead.
Source: Energy density - Wikipedia
Diesel
| Specific Energy of Diesel kWh/l | 10.7222 |
| Efficiency Factor % (30-40) | 35 |
| Diesel kWh/l - after Efficiency Factor | 3.75277 |
| Diesel l/kWh - after Efficiency Factor | 0.26647 |
Hydrogen
| Specific Energy of Hydrogen kWh/kg | 33.3139 |
| Efficiency Factor % (40-60) | 50 |
| Hydrogen kWh/kg - after Efficiency Factor | 16.65695 |
| Hydrogen kg/kWh - after Efficiency Factor |
0.060035 |
The Max Fuel used by a truck can be calculated using the engine power.
Max Fuel (l/hr) = Gross Engine Power (kW) / (Specific Energy (kWh/l) x Efficiency Factor (%))
Idle Fuel = Max Fuel (l/hr) * 5%
Diesel Mechanical

Diesel Electric

Diesel Electric Hybrid

Hydrogen Electric Hybrid

Battery Electric Hybrid

Regenerative Braking (Vehicles with Batteries)
| Diesel Engine (Diesel to RPM) | In Diesel/Mechanical Energy, diesel engine converts diesel fuel to mechanical energy in the form of RPM at the flywheel. |
| Torque Converter (RPM to RPM) | Provides a fluid coupling to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. |
| Transmission (RPM to RPM) | Uses gears to change the ratio between the rotation speed of the engine and the wheels. |
| Differential (RPM to RPM) | Transfers the rotation from the drive shaft to the axle. |
| Axle (RPM to RPM) | Transfers energy from the differential to the wheels. |
| Alternator (RPM to AC) | The alternator is used to make Electrical Energy (AC) from mechanical energy. |
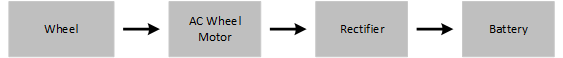
| Rectifier (AC to DC) | A rectifier is used to convert Alternating Current (AC) to Direct Current (DC). |
| Inverter (DC to AC) | An inverter is used to convert Direct Current to Alternating Current. |
| AC to Wheel Motor (AC to Wheel) | The AC Wheel Motor converts AC electricity to rotational energy at the wheel. |
| Battery (DC) | Used to store electrical energy. |
| Fuel Cell (H2 to DC) | Used to convert Hydrogen to electrical energy. |