Definition of hours |

|
|
|
Definition of hours |

|

|
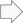
To understand how XPAC determines the capacity of a resource, you must first understand how the hours are defined and derived for a resource. The terminology used for hours is described below.
The starting point for calculating the resource hours is the calendar hours in the time period. This is the total elapsed time between the start date (and time) for the current period and the start date (and time) for the following period.
The roster hours are determined by overlaying the roster assigned to the resource over the calendar time. For example, consider a roster which operates 24 hours a day Monday to Friday and not at all on Saturday or Sunday. When this roster is overlayed on the calendar time in the time period, each Monday to Friday is added up to calculate the total roster hours.
The fixed delay hours include all of the Roster Exceptions that occur within the time period. The fixed delay hours may be allocated as either operating or non-operating hours.
Roster Exceptions can be assigned as extended operation delay types. An extended operation is time which is available for the resource despite the normal roster that has been specified. For example, overtime could be entered as an extended operation.
The planned hours are calculated by subtracting the Fixed Delay Hours from the Roster Hours and then adding the Extended Operation Hours.
The current availability and resource utilisation are used to represent unfixed delay hours which are expressed as a percentage. These percentages are applied to the Planned Hours.
The period delays are used to store the unfixed delay hours which are entered as a fixed number of hours for the time period.
The Operating Hours are calculated by subtracting the Period Delay Hours from the Planned Hours, and then multiplying the result by the Availability and Utilisation. The Fixed Operating Delay Hours are then added back in (ie. the Roster Exceptions which are operating delays).
The Work Hours are those Operating Hours which are spent on productive activities, ie. scheduling records as opposed to delays. The Work Hours are calculated by subtracting the Fixed Operating Delays (ie. the Roster Exceptions which are operating delays) and the In Path Operating Delays from the Operating Hours.