Example XCMs to read parameters |

|
|
|
Example XCMs to read parameters |

|

|
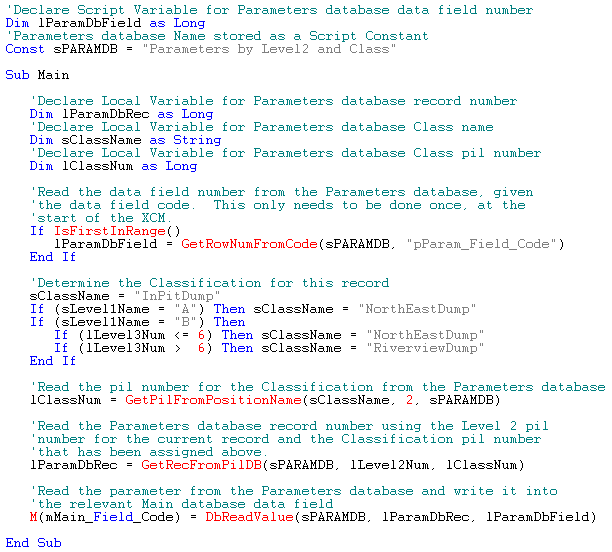
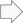
The following example XCM is run over the Main database. It reads a value from a Parameters database and writes it into the current record in the Main database. It is assumed that the Main database has 4 levels, called Level1, Level2, Level3 and Level4.
In this first example, the Parameters database has two levels, namely Level1 and Level4 from the Main database.
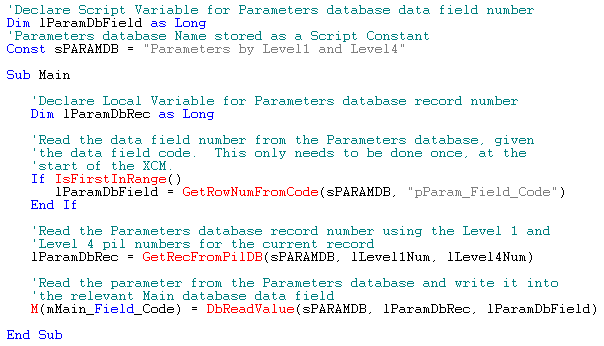
The following example XCM is run over the Main database. It reads a value from a Parameters database and writes it into the current record in the Main database. It is assumed that the Main database has 4 levels, called Level1, Level2, Level3 and Level4.
In this second example, the Parameters database has two levels, namely Level2 from the Main database and a Classification. The Classification could be a waste dump destination, a product type, a dragline digging methodology, a seam group, etc. This example assumes that the Classification level in the Parameters database is level 2 and a position table has been defined for this level.