Proximity constraints |

|
|
|
Proximity constraints |

|

|
Use proximity constraints to control the interaction between resources that have been assigned to blocks in similar section of the mine. They can:
| • | Limit the number of resources allowed to work in any block at the same time, within a particular range (e.g. a geographical area) |
| • | Limit the number of resources allowed to work in and section of the mine, within a particular range (ie a longwall gateroad) |
| • | Define the impact that multiple resources working in proximity to one another will have on production rate of itself and other resources (e.g. two or three continuous miners working together in a multi-heading drive). |
You can assign a number of proximity constraint sets to each scenario; and each set can contain several proximity constraints. We nevertheless recommend limiting the number of constraints per constraint set, as it makes it clearer which constraints are being applied.
Option |
Description |
||
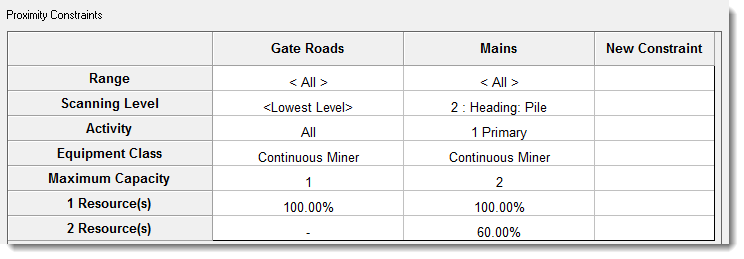
Range |
Constraints are applied to a main database range. |
||
Scanning Level |
The level of the database used to split the range into sections. Each section will be treated as if it has a separate constraint, so even if there are 4 sections, you only require one constraint. |
||
Activity |
Constraints can be applied to all or a single productive activity within the database range. |
||
Resource Class |
Constraints are applied to a resource class, it is not possible at present to control the interaction between resources that have been defined as different resource classes. |
||
Maximum Capacity |
Defines the maximum number of resources that can be mining in the same scheduling block simultaneously. |
||
1 Resource |
|
||
<x> Resources |
This defines the percentage of the production rate that each machine will work at when there are x number in the same block. For example, if two machines are working in the same block at the same time, then each will work at 60% of its normal production rate. |