Importing and exporting spatial data |

|
|
|
Importing and exporting spatial data |

|

|
XPAC lets you import and export spatial data from a number of sources, for example, geological modelling programs, fixed width and delimited files, and other XPAC projects so that you can create spatial data plots using the tools available in XPAC. For example, you may want to export spatial data from Vulcan, or share spatial data between XPAC projects.
When importing or exporting spatial data as fixed width or delimited files, you can also use settings templates or the Field Setup Wizard to save you time. Once you have imported spatial data, you may want to use them in other XPAC projects. Instead of transferring data using an external file type, you can transfer XPAC spatial data sets using XPAC template files (see Importing and exporting XPAC spatial data sets for more information).
XPAC makes a distinction between 2D and 3D spatial data:
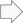
XPAC defines a polygon as a two-dimensional shape consisting of at least three vertices (points) connected by straight lines. Although 2D (have no 'thickness'), polygons can still exist in XPAC in a three-dimensional space (they can exist in any orientation). Multiple polygons in different orientations can be grouped together to represent three-dimensional shapes. For example, six polygons can be used to represent a cube. A single polygon must have at least three vertices (points) to form a triangle, but may have multiple vertices to form more complex shapes.
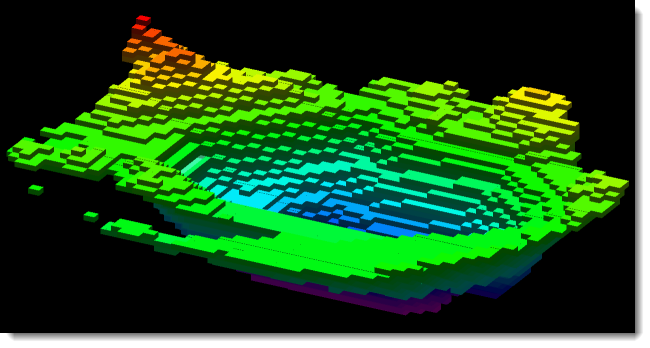
XPAC defines a solid as a triangulation representing a closed surface consisting of a series of vertices (points) and triplets of indexes into the series of vertices to represent triangles. A solid exists in three-dimensional space in any orientation and can be arbitrarily complex.
|
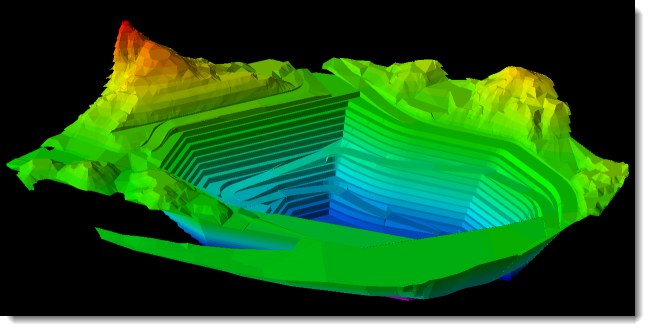
You can create a solid from a polygon by defining an extrusion, or by creating the solid in an external geological design package such as Vulcan before importing it into XPAC. |